Understanding python classes
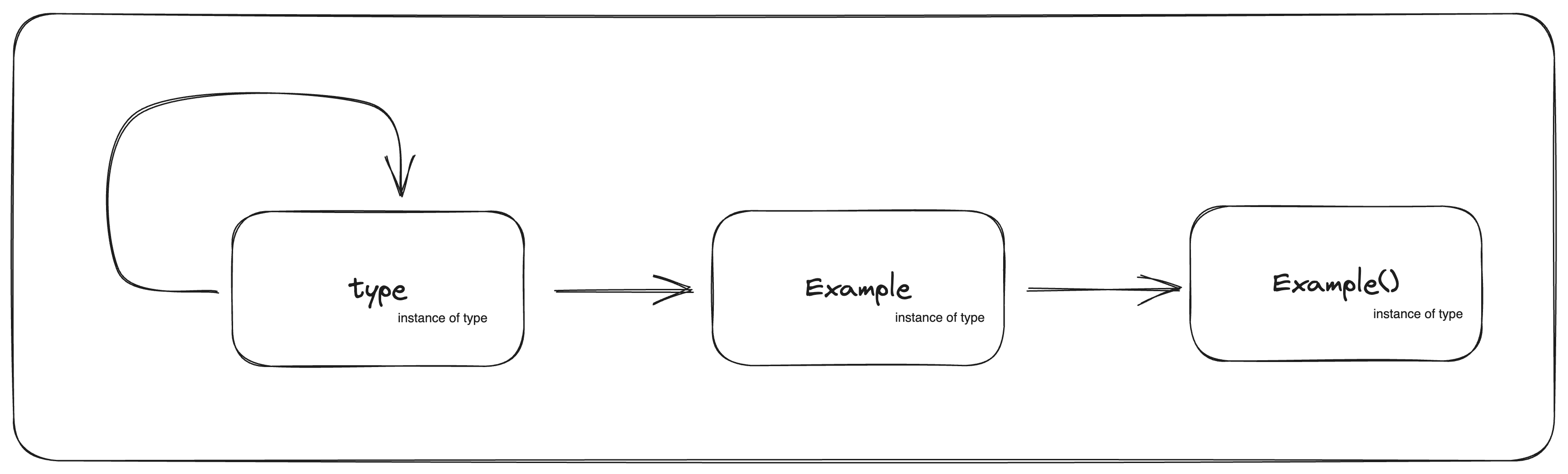
Every object in python has a type, and type(obj) == obj.class
class Example:
attr = 1
def method(self):
return "method"
print(f"{type(44)=}") # type(44)=<class 'int'>
print(f"{type('hello')=}") # type('hello')=<class 'str'>
print(f"{type(())=}") # type(())=<class 'tuple'>
print(f"{type([])=}") # type([])=<class 'list'>
print(f"{Example.__class__=}") # <class 'type'>
print(f"{type(Example)=}") # <class 'type'>
print(f"{type(type(type))=}") # <class 'type'>
print(f"{Example().__class__=}") # <class '__main__.Example'>
assert isinstance(Example, type)
assert isinstance(Example(), Example)
Last update: June 2, 2023
Created: June 2, 2023
Created: June 2, 2023